Installing MXNet¶
Indicate your preferred configuration. Then, follow the customized commands to install MXNet.
$ pip install mxnet
MKL-DNN enabled pip packages are optimized for Intel hardware. You can find performance numbers in the MXNet tuning guide.
$ pip install mxnet-mkl
$ pip install mxnet==1.4.1
MKL-DNN enabled pip packages are optimized for Intel hardware. You can find performance numbers in the MXNet tuning guide.
$ pip install mxnet-mkl==1.4.1
$ pip install mxnet==1.3.1
MKL-DNN enabled pip packages are optimized for Intel hardware. You can find performance numbers in the MXNet tuning guide.
$ pip install mxnet-mkl==1.3.1
$ pip install mxnet==1.2.1
MKL-DNN enabled pip packages are optimized for Intel hardware. You can find performance numbers in the MXNet tuning guide.
$ pip install mxnet-mkl==1.2.1
$ pip install mxnet==1.1.0
$ pip install mxnet==1.0.0
$ pip install mxnet==0.12.1
For MXNet 0.12.0:
$ pip install mxnet==0.12.0
$ pip install mxnet==0.11.0
$ pip install mxnet --pre
MKL-DNN enabled pip packages are optimized for Intel hardware. You can find performance numbers in the MXNet tuning guide.
$ pip install mxnet-mkl --pre
Check the chart below for other options, refer to PyPI for other MXNet pip packages, or validate your MXNet installation.
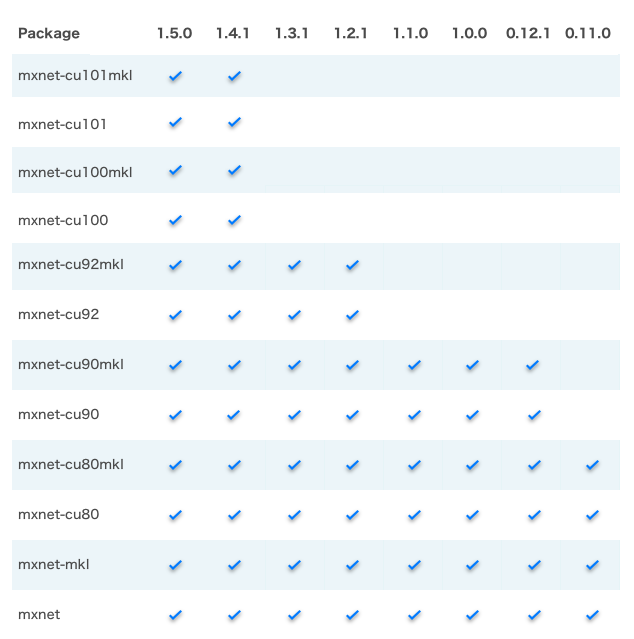
NOTES:
mxnet-cu101mkl means the package is built with CUDA/cuDNN and MKL-DNN enabled and the CUDA version is 10.1.
All MKL pip packages are experimental prior to version 1.3.0.
Docker images with MXNet are available at Docker Hub.
Step 1 Install Docker on your machine by following the docker installation instructions.
Note - You can install Community Edition (CE) to get started with MXNet.
Step 2 [Optional] Post installation steps to manage Docker as a non-root user.
Follow the four steps in this docker documentation to allow managing docker containers without sudo.
If you skip this step, you need to use sudo each time you invoke Docker.
Step 3 Pull the MXNet docker image.
$ docker pull mxnet/python # Use sudo if you skip Step 2
You can list docker images to see if mxnet/python docker image pull was successful.
$ docker images # Use sudo if you skip Step 2
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
mxnet/python latest 00d026968b3c 3 weeks ago 1.41 GB
Using the latest MXNet with Intel MKL-DNN is recommended for the fastest inference speeds with MXNet.
$ docker pull mxnet/python:1.3.0_cpu_mkl # Use sudo if you skip Step 2
$ docker images # Use sudo if you skip Step 2
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
mxnet/python 1.3.0_cpu_mkl deaf9bf61d29 4 days ago 678 MB
Step 4 Validate the installation.
To build from source, refer to the MXNet Ubuntu installation guide.
$ pip install mxnet-cu101
$ pip install mxnet-cu101==1.4.1
$ pip install mxnet-cu92==1.3.1
$ pip install mxnet-cu92==1.2.1
$ pip install mxnet-cu91==1.1.0
$ pip install mxnet-cu90==1.0.0
$ pip install mxnet-cu90==0.12.1
$ pip install mxnet-cu80==0.11.0
$ pip install mxnet-cu101 --pre
MXNet offers MKL pip packages that will be much faster when running on Intel hardware. Check the chart below for other options, refer to PyPI for other MXNet pip packages, or validate your MXNet installation.

NOTES:
mxnet-cu101mkl means the package is built with CUDA/cuDNN and MKL-DNN enabled and the CUDA version is 10.1.
All MKL pip packages are experimental prior to version 1.3.0.
CUDA should be installed first. Instructions can be found in the CUDA dependencies section of the MXNet Ubuntu installation guide.
Important: Make sure your installed CUDA version matches the CUDA version in the pip package. Check your CUDA version with the following command:
nvcc --version
You can either upgrade your CUDA install or install the MXNet package that supports your CUDA version.
Docker images with MXNet are available at Docker Hub.
Step 1 Install Docker on your machine by following the docker installation instructions.
Note - You can install Community Edition (CE) to get started with MXNet.
Step 2 [Optional] Post installation steps to manage Docker as a non-root user.
Follow the four steps in this docker documentation to allow managing docker containers without sudo.
If you skip this step, you need to use sudo each time you invoke Docker.
Step 3 Install nvidia-docker-plugin following the installation instructions. nvidia-docker-plugin is required to enable the usage of GPUs from the docker containers.
Step 4 Pull the MXNet docker image.
$ docker pull mxnet/python:gpu # Use sudo if you skip Step 2
You can list docker images to see if mxnet/python docker image pull was successful.
$ docker images # Use sudo if you skip Step 2
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
mxnet/python gpu 493b2683c269 3 weeks ago 4.77 GB
Using the latest MXNet with Intel MKL-DNN is recommended for the fastest inference speeds with MXNet.
$ docker pull mxnet/python:1.3.0_cpu_mkl # Use sudo if you skip Step 2
$ docker images # Use sudo if you skip Step 2
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
mxnet/python 1.3.0_gpu_cu92_mkl adcb3ab19f50 4 days ago 4.23 GB
Step 5 Validate the installation.
Refer to the MXNet Ubuntu installation guide.
The default version of R that is installed with apt-get is insufficient. You will need to first install R v3.4.4+ and build MXNet from source.
After you have setup R v3.4.4+ and MXNet, you can build and install the MXNet R bindings with the following, assuming that incubator-mxnet is the source directory you used to build MXNet as follows:
$ cd incubator-mxnet
$ make rpkg
The default version of R that is installed with apt-get is insufficient. You will need to first install R v3.4.4+ and build MXNet from source.
After you have setup R v3.4.4+ and MXNet, you can build and install the MXNet R bindings with the following, assuming that incubator-mxnet is the source directory you used to build MXNet as follows:
$ cd incubator-mxnet
$ make rpkg
You can use the Maven packages defined in the following dependency to include MXNet in your Scala project. Please refer to the MXNet-Scala setup guide for a detailed set of instructions to help you with the setup process.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.mxnet</groupId>
<artifactId>mxnet-full_2.11-linux-x86_64-gpu</artifactId>
</dependency>
You can use the Maven packages defined in the following dependency to include MXNet in your Scala project. Please refer to the MXNet-Scala setup guide for a detailed set of instructions to help you with the setup process.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.mxnet</groupId>
<artifactId>mxnet-full_2.11-linux-x86_64-cpu</artifactId>
</dependency>
You can use the Maven packages defined in the following dependency to include MXNet in your Clojure project. To maximize leverage, the Clojure package has been built on the existing Scala package. Please refer to the MXNet-Scala setup guide for a detailed set of instructions to help you with the setup process that is required to use the Clojure dependency.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.mxnet.contrib.clojure</groupId>
<artifactId>clojure-mxnet-linux-gpu</artifactId>
</dependency>
You can use the Maven packages defined in the following dependency to include MXNet in your Clojure project. To maximize leverage, the Clojure package has been built on the existing Scala package. Please refer to the MXNet-Scala setup guide for a detailed set of instructions to help you with the setup process that is required to use the Clojure dependency.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.mxnet.contrib.clojure</groupId>
<artifactId>clojure-mxnet-linux-cpu</artifactId>
</dependency>
You can use the Maven packages defined in the following dependency to include MXNet in your Java project. The Java API is provided as a subset of the Scala API and is intended for inference only. Please refer to the MXNet-Java setup guide for a detailed set of instructions to help you with the setup process.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.mxnet</groupId>
<artifactId>mxnet-full_2.11-linux-x86_64-gpu</artifactId>
<version>[1.5.0, )</version>
</dependency>
You can use the Maven packages defined in the following dependency to include MXNet in your Java project. The Java API is provided as a subset of the Scala API and is intended for inference only. Please refer to the MXNet-Java setup guide for a detailed set of instructions to help you with the setup process.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.mxnet</groupId>
<artifactId>mxnet-full_2.11-linux-x86_64-cpu</artifactId>
<version>[1.5.0, )</version>
</dependency>
To enable the C++ package, build from source using `make USE_CPP_PACKAGE=1`.
Refer to the MXNet C++ setup guide for more info.
$ pip install mxnet
$ pip install mxnet==1.4.1
$ pip install mxnet==1.3.1
$ pip install mxnet==1.2.1
$ pip install mxnet==1.1.0
$ pip install mxnet==1.0.0
$ pip install mxnet=0.12.1
$ pip install mxnet==0.11.0
$ pip install mxnet --pre
MXNet offers MKL pip packages that will be much faster when running on Intel hardware. Check the chart below for other options, refer to PyPI for other MXNet pip packages, or validate your MXNet installation.

NOTES:
mxnet-cu101mkl means the package is built with CUDA/cuDNN and MKL-DNN enabled and the CUDA version is 10.1.
All MKL pip packages are experimental prior to version 1.3.0.
Docker images with MXNet are available at Docker Hub.
Step 1 Install Docker on your machine by following the docker installation instructions.
Note - You can install Community Edition (CE) to get started with MXNet.
Step 2 Pull the MXNet docker image.
$ docker pull mxnet/python
You can list docker images to see if mxnet/python docker image pull was successful.
$ docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
mxnet/python latest 00d026968b3c 3 weeks ago 1.41 GB
Using the latest MXNet with Intel MKL-DNN is recommended for the fastest inference speeds with MXNet.
$ docker pull mxnet/python:1.3.0_cpu_mkl # Use sudo if you skip Step 2
$ docker images # Use sudo if you skip Step 2
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
mxnet/python 1.3.0_cpu_mkl deaf9bf61d29 4 days ago 678 MB
Step 4 Validate the installation.
To build from source, refer to the MXNet macOS installation guide.
MXNet developers should refer to the MXNet wiki’s Developer Setup on Mac.
Refer to the MXNet macOS installation guide.
MXNet developers should refer to the MXNet wiki’s Developer Setup on Mac.
To run MXNet you also should have OpenCV and OpenBLAS installed. You may install them with brew as follows:
brew install opencv
brew install openblas
To ensure MXNet R package runs with the version of OpenBLAS installed, create a symbolic link as follows:
ln -sf /usr/local/opt/openblas/lib/libopenblas.dylib /usr/local/opt/openblas/lib/libopenblasp-r0.3.1.dylib
Note: packages for 3.6.x are not yet available.
Install 3.5.x of R from CRAN. The latest is v3.5.3.
You can build MXNet-R from source, or you can use a pre-built binary:
cran <- getOption("repos")
cran["dmlc"] <- "https://apache-mxnet.s3-accelerate.dualstack.amazonaws.com/R/CRAN/"
options(repos = cran)
install.packages("mxnet")
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.mxnet</groupId>
<artifactId>mxnet-full_2.11-osx-x86_64-cpu</artifactId>
</dependency>
Not available at this time.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.mxnet.contrib.clojure</groupId>
<artifactId>clojure-mxnet-osx-cpu</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.mxnet</groupId>
<artifactId>mxnet-full_2.11-linux-x86_64-cpu</artifactId>
<version>[1.5.0, )</version>
</dependency>
Not available at this time.
To enable the C++ package, build from source using `make USE_CPP_PACKAGE=1`.
Refer to the MXNet C++ setup guide for more info.
For more installation options, refer to the MXNet macOS installation guide.
$ pip install mxnet
$ pip install mxnet==1.4.1
$ pip install mxnet==1.3.1
$ pip install mxnet==1.2.1
$ pip install mxnet==1.1.0
$ pip install mxnet==1.0.0
$ pip install mxnet==0.12.1
$ pip install mxnet==0.11.0
$ pip install mxnet --pre
MXNet offers MKL pip packages that will be much faster when running on Intel hardware. Check the chart below for other options, refer to PyPI for other MXNet pip packages, or validate your MXNet installation.

NOTES:
mxnet-cu101mkl means the package is built with CUDA/cuDNN and MKL-DNN enabled and the CUDA version is 10.1.
All MKL pip packages are experimental prior to version 1.3.0.
Docker images with MXNet are available at Docker Hub.
Step 1 Install Docker on your machine by following the docker installation instructions.
Note - You can install Community Edition (CE) to get started with MXNet.
Step 2 [Optional] Post installation steps to manage Docker as a non-root user.
Follow the four steps in this docker documentation to allow managing docker containers without sudo.
If you skip this step, you need to use sudo each time you invoke Docker.
Step 3 Pull the MXNet docker image.
$ docker pull mxnet/python # Use sudo if you skip Step 2
You can list docker images to see if mxnet/python docker image pull was successful.
$ docker images # Use sudo if you skip Step 2
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
mxnet/python latest 00d026968b3c 3 weeks ago 1.41 GB
Using the latest MXNet with Intel MKL-DNN is recommended for the fastest inference speeds with MXNet.
$ docker pull mxnet/python:1.3.0_cpu_mkl # Use sudo if you skip Step 2
$ docker images # Use sudo if you skip Step 2
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
mxnet/python 1.3.0_cpu_mkl deaf9bf61d29 4 days ago 678 MB
Step 4 Validate the installation.
Refer to the MXNet Windows installation guide
$ pip install mxnet-cu101
$ pip install mxnet-cu101==1.4.1
$ pip install mxnet-cu92==1.3.1
$ pip install mxnet-cu92==1.2.1
$ pip install mxnet-cu91==1.1.0
$ pip install mxnet-cu90==1.0.0
$ pip install mxnet-cu90==0.12.1
$ pip install mxnet-cu80==0.11.0
$ pip install mxnet-cu101 --pre
MXNet offers MKL pip packages that will be much faster when running on Intel hardware. Check the chart below for other options, refer to PyPI for other MXNet pip packages, or validate your MXNet installation.

NOTES:
mxnet-cu101mkl means the package is built with CUDA/cuDNN and MKL-DNN enabled and the CUDA version is 10.1.
All MKL pip packages are experimental prior to version 1.3.0.
Anaconda is recommended.
CUDA should be installed first. Instructions can be found in the CUDA dependencies section of the MXNet Ubuntu installation guide.
Important: Make sure your installed CUDA version matches the CUDA version in the pip package. Check your CUDA version with the following command:
nvcc --version
Refer to #8671 for status on CUDA 9.1 support.
You can either upgrade your CUDA install or install the MXNet package that supports your CUDA version.
To build from source, refer to the MXNet Windows installation guide.
Note: packages for 3.6.x are not yet available. Install 3.5.x of R from CRAN.
You can build MXNet-R from source, or you can use a pre-built binary:
cran <- getOption("repos")
cran["dmlc"] <- "https://apache-mxnet.s3-accelerate.dualstack.amazonaws.com/R/CRAN/"
options(repos = cran)
install.packages("mxnet")
To run MXNet you also should have OpenCV and OpenBLAS installed.
You can build MXNet-R from source, or you can use a pre-built binary:
cran <- getOption("repos")
cran["dmlc"] <- "https://apache-mxnet.s3-accelerate.dualstack.amazonaws.com/R/CRAN/GPU/cu92"
options(repos = cran)
install.packages("mxnet")
Change cu92 to cu90, cu91 or cuda100 based on your CUDA toolkit version. Currently, MXNet supports these versions of CUDA. Note : You also need to have cuDNN installed on Windows. Check out this guide on the steps for installation.
MXNet-Scala for Windows is not yet available.
MXNet-Clojure for Windows is not yet available.
MXNet-Java for Windows is not yet available.
To enable the C++ package, build from source using `make USE_CPP_PACKAGE=1`.
Refer to the MXNet C++ setup guide for more info.
For more installation options, refer to the MXNet Windows installation guide.
MXNet is available on several cloud providers with GPU support. You can also find GPU/CPU-hybrid support for use cases like scalable inference, or even fractional GPU support with AWS Elastic Inference.
Alibaba
Amazon Web Services
- Amazon SageMaker - Managed training and deployment of MXNet models
- AWS Deep Learning AMI - Preinstalled Conda environments for Python 2 or 3 with MXNet, CUDA, cuDNN, MKL-DNN, and AWS Elastic Inference
- Dynamic Training on AWS - experimental manual EC2 setup or semi-automated CloudFormation setup
- NVIDIA VM
Google Cloud Platform
Microsoft Azure
Oracle Cloud
All NVIDIA VMs use the NVIDIA MXNet Docker container. Follow the container usage instructions found in NVIDIA’s container repository.
- Amazon Web Services
- AWS Deep Learning AMI - Preinstalled Conda environments for Python 2 or 3 with MXNet and MKL-DNN.
MXNet supports the Debian based Raspbian ARM based operating system so you can run MXNet on Raspberry Pi 3B devices.
These instructions will walk through how to build MXNet for the Raspberry Pi and install the Python bindings for the library.
You can do a dockerized cross compilation build on your local machine or a native build on-device.
The complete MXNet library and its requirements can take almost 200MB of RAM, and loading large models with the library can take over 1GB of RAM. Because of this, we recommend running MXNet on the Raspberry Pi 3 or an equivalent device that has more than 1 GB of RAM and a Secure Digital (SD) card that has at least 4 GB of free memory.
Quick installation¶
You can use this pre-built Python wheel on a Raspberry Pi 3B with Stretch. You will likely need to install several dependencies to get MXNet to work. Refer to the following Build section for details.
Docker installation¶
Step 1 Install Docker on your machine by following the docker installation instructions.
Note - You can install Community Edition (CE)
Step 2 [Optional] Post installation steps to manage Docker as a non-root user.
Follow the four steps in this docker documentation to allow managing docker containers without sudo.
Build¶
This cross compilation build is experimental.
Please use a Native build with gcc 4 as explained below, higher compiler versions currently cause test failures on ARM.
The following command will build a container with dependencies and tools,
and then compile MXNet for ARMv7.
You will want to run this on a fast cloud instance or locally on a fast PC to save time.
The resulting artifact will be located in build/mxnet-x.x.x-py2.py3-none-any.whl.
Copy this file to your Raspberry Pi.
The previously mentioned pre-built wheel was created using this method.
ci/build.py -p armv7
Install using a pip wheel¶
Your Pi will need several dependencies.
Install MXNet dependencies with the following:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y \
apt-transport-https \
build-essential \
ca-certificates \
cmake \
curl \
git \
libatlas-base-dev \
libcurl4-openssl-dev \
libjemalloc-dev \
liblapack-dev \
libopenblas-dev \
libopencv-dev \
libzmq3-dev \
ninja-build \
python-dev \
python-pip \
software-properties-common \
sudo \
unzip \
virtualenv \
wget
Install virtualenv with:
sudo pip install virtualenv
Create a Python 2.7 environment for MXNet with:
virtualenv -p `which python` mxnet_py27
You may use Python 3, however the wine bottle detection example for the Pi with camera requires Python 2.7.
Activate the environment, then install the wheel we created previously, or install this prebuilt wheel.
source mxnet_py27/bin/activate
pip install mxnet-x.x.x-py2.py3-none-any.whl
Test MXNet with the Python interpreter:
$ python
>>> import mxnet
If there are no errors then you’re ready to start using MXNet on your Pi!
Native Build¶
Installing MXNet from source is a two-step process:
- Build the shared library from the MXNet C++ source code.
- Install the supported language-specific packages for MXNet.
Step 1 Build the Shared Library
On Raspbian versions Wheezy and later, you need the following dependencies:
- Git (to pull code from GitHub)
- libblas (for linear algebraic operations)
- libopencv (for computer vision operations. This is optional if you want to save RAM and Disk Space)
- A C++ compiler that supports C++ 11. The C++ compiler compiles and builds MXNet source code. Supported compilers include the following:
- G++ (4.8 or later). Make sure to use gcc 4 and not 5 or 6 as there are known bugs with these compilers.
- Clang (3.9 - 6)
Install these dependencies using the following commands in any directory:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get -y install git cmake ninja-build build-essential g++-4.9 c++-4.9 liblapack* libblas* libopencv* libopenblas* python3-dev python-dev virtualenv
Clone the MXNet source code repository using the following git command in your home directory:
git clone https://github.com/apache/incubator-mxnet.git --recursive
cd incubator-mxnet
Build:
mkdir -p build && cd build
cmake \
-DUSE_SSE=OFF \
-DUSE_CUDA=OFF \
-DUSE_OPENCV=ON \
-DUSE_OPENMP=ON \
-DUSE_MKL_IF_AVAILABLE=OFF \
-DUSE_SIGNAL_HANDLER=ON \
-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release \
-GNinja ..
ninja -j$(nproc)
Some compilation units require memory close to 1GB, so it’s recommended that you enable swap as explained below and be cautious about increasing the number of jobs when building (-j)
Executing these commands start the build process, which can take up to a couple hours, and creates a file called libmxnet.so in the build directory.
If you are getting build errors in which the compiler is being killed, it is likely that the compiler is running out of memory (especially if you are on Raspberry Pi 1, 2 or Zero, which have less than 1GB of RAM), this can often be rectified by increasing the swapfile size on the Pi by editing the file /etc/dphys-swapfile and changing the line CONF_SWAPSIZE=100 to CONF_SWAPSIZE=1024, then running:
sudo /etc/init.d/dphys-swapfile stop
sudo /etc/init.d/dphys-swapfile start
free -m # to verify the swapfile size has been increased
Step 2 Build cython modules (optional)
$ pip install Cython
$ make cython # You can set the python executable with `PYTHON` flag, e.g., make cython PYTHON=python3
MXNet tries to use the cython modules unless the environment variable MXNET_ENABLE_CYTHON is set to 0. If loading the cython modules fails, the default behavior is falling back to ctypes without any warning. To raise an exception at the failure, set the environment variable MXNET_ENFORCE_CYTHON to 1. See here for more details.
Step 3 Install MXNet Python Bindings
To install Python bindings run the following commands in the MXNet directory:
cd python
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -e .
Note that the -e flag is optional. It is equivalent to --editable and means that if you edit the source files, these changes will be reflected in the package installed.
Alternatively you can create a whl package installable with pip with the following command:
ci/docker/runtime_functions.sh build_wheel python/ $(realpath build)
You are now ready to run MXNet on your Raspberry Pi device. You can get started by following the tutorial on Real-time Object Detection with MXNet On The Raspberry Pi.
Note - Because the complete MXNet library takes up a significant amount of the Raspberry Pi’s limited RAM, when loading training data or large models into memory, you might have to turn off the GUI and terminate running processes to free RAM.
Nvidia Jetson TX family¶
MXNet supports the Ubuntu Arch64 based operating system so you can run MXNet on NVIDIA Jetson Devices.
These instructions will walk through how to build MXNet for the Pascal based NVIDIA Jetson TX2 and install the corresponding python language bindings.
For the purposes of this install guide we will assume that CUDA is already installed on your Jetson device.
Install MXNet
Installing MXNet is a two-step process:
- Build the shared library from the MXNet C++ source code.
- Install the supported language-specific packages for MXNet.
Step 1 Build the Shared Library
You need the following additional dependencies:
- Git (to pull code from GitHub)
- libatlas (for linear algebraic operations)
- libopencv (for computer vision operations)
- python pip (to load relevant python packages for our language bindings)
Install these dependencies using the following commands in any directory:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get -y install git build-essential libatlas-base-dev libopencv-dev graphviz python-pip
sudo pip install pip --upgrade
sudo pip install setuptools numpy --upgrade
sudo pip install graphviz==0.8.4 \
jupyter
Clone the MXNet source code repository using the following git command in your home directory:
git clone https://github.com/apache/incubator-mxnet.git --recursive
cd incubator-mxnet
Edit the Makefile to install the MXNet with CUDA bindings to leverage the GPU on the Jetson:
cp make/crosscompile.jetson.mk config.mk
Edit the Mshadow Makefile to ensure MXNet builds with Pascal’s hardware level low precision acceleration by editing 3rdparty/mshadow/make/mshadow.mk and adding the following after line 122:
MSHADOW_CFLAGS += -DMSHADOW_USE_PASCAL=1
Now you can build the complete MXNet library with the following command:
make -j $(nproc)
Executing this command creates a file called libmxnet.so in the mxnet/lib directory.
Step 2 Install MXNet Python Bindings
To install Python bindings run the following commands in the MXNet directory:
cd python
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -e .
Note that the -e flag is optional. It is equivalent to --editable and means that if you edit the source files, these changes will be reflected in the package installed.
Add the mxnet folder to the path:
cd ..
export MXNET_HOME=$(pwd)
echo "export PYTHONPATH=$MXNET_HOME/python:$PYTHONPATH" >> ~/.rc
source ~/.rc
You are now ready to run MXNet on your NVIDIA Jetson TX2 device.
Source Download¶
Download your required version of MXNet and build from source.




